Troubleshooting FortiGate VPN Tunnels: A Comprehensive Guide
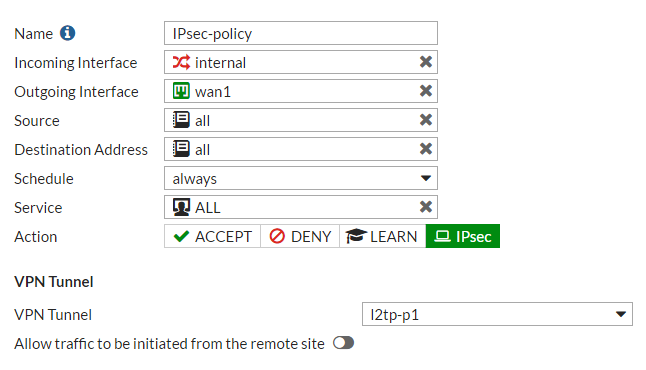
Establishing a secure VPN tunnel between FortiGate firewalls is important for enabling secure remote access and site-to-site connectivity. However, issues can arise during the setup or operation of these tunnels, calling for thorough troubleshooting. This guide will walk you through the process of identifying and resolving common VPN tunnel problems on FortiGate devices.
1. Verify VPN Tunnel Status
The first step is to check the current status of the VPN tunnel. You can do this using this command:
get vpn ipsec tunnel summary
This will display a list of configured VPN tunnels and their current state (up or down).[2]
2. Check Phase 1 (IKE) Status
If the tunnel is down, the next step is to investigate the Phase 1 (IKE) status using:
diagnose vpn ike gateway list
Look for the status field, which should ideally show established. If it shows connecting or any other state, there is a Phase 1 issue.[2]
Common Phase 1 issues include:
- Mismatched Pre-Shared Key (PSK): Ensure the PSK matches exactly between the peers.[3]
- Proposal Mismatch: Check that the Phase 1 encryption, authentication, and DH group settings match on both ends.[3]
- Network Connectivity: Use
tracerouteto verify network connectivity between the VPN peers.[2]
execute traceroute 10.1.1.1 source 192.168.1.1- NAT Traversal Settings: Ensure NAT traversal is enabled/disabled consistently on both ends.[4]
3. Debug Phase 1 Negotiation
To further investigate Phase 1 issues, enable IKE debugging:
diagnose vpn ike log-filter dst-addr4 <remote_peer_ip>
diagnose debug app ike -1
diagnose debug enable
This will show the IKE negotiation process and any errors or mismatches between the peers.[2][5]
4. Check Phase 2 (IPsec) Status
If Phase 1 is established, check the Phase 2 status using:
diagnose vpn tunnel list name <tunnel_name>
Look for the tunnel entry and ensure the stat field shows traffic counters incrementing.[2]
Common Phase 2 issues include:
- Proposal Mismatch: Verify that the Phase 2 encryption and authentication settings match on both ends.[3]
- Policy Mismatch: Check that the source, destination, service, and action settings in the VPN policies match.[4]
- Routing: Ensure static routes are configured correctly to route VPN traffic properly.[1]
- MTU Size: Check for MTU issues by looking for "fragment" messages in the tunnel stats.[4]
5. Debug Phase 2 Negotiation
To debug Phase 2 issues, enable IPsec debugging:
diagnose debug application ipsecengine -1
diagnose debug enable
This will show the Phase 2 negotiation process and any errors or mismatches.[5]
6. Packet Capture
If all else fails, perform a packet capture to analyze the traffic:
diagnose sniffer packet any 'host <remote_peer_ip> and port 500'
This will capture IKE (UDP 500) packets, which can help identify issues like blocked traffic or incorrect packet contents.[1][5]
By following these steps and investigating the various variables involved, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve issues with FortiGate VPN tunnels, ensuring secure and reliable connectivity.
Citations:
[1] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=91GznQt2kzg&t=0
[2] https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiGate/Troubleshooting-Tip-IPsec-VPNs-tunnels/ta-p/195955
[3] https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/5.4.0/cookbook/168495/ipsec-vpn-troubleshooting
[4] https://www.fortinetguru.com/2019/07/troubleshooting-ipsec/
[5] https://ipsec118.rssing.com/chan-69458736/article14.html